Hacking has made the headlines and been prominent ever since the birth of cryptocurrency. By definition, the same talent and people will want to cause disruption as well as pioneer a new way of society.

A study conducted by the American company Foley & Lardner showed that 71% of large cryptocurrency traders and investors attribute theft of cryptocurrency to the strongest risk that negatively affects the market. 31% reported hackers’ activity threat to the global cryptocurrency industry as very high.
Hacking can be placed in to 3 categories:
- Attacks on the blockchains, cryptocurrency exchanges and ICOs;
- Distribution of software for hidden mining;
- Attacks directed at users’ wallets.
According to research conducted by ING Bank NV and Ipsos, about 9% of Europeans and 8% of U.S. residents own cryptocurrencies, with 25% of the population planning to buy digital assets in the near future. Thus, almost a quarter of a billion potential victims could soon fall into the field of hacking activity.
Apps
We all have them and we all like and with smartphones, we all need them. Victims of hacking are most often smartphone owners specifically with the Android operating system. Usually, without Two Factor Authentication (2FA) — this requires not only a password and username but also something that user has on them, i.e., a piece of information only they could know or have on hand immediately, such as a physical token.
The reason being is that Google Android’s open operating system makes it more open to viruses, and therefore less safe than the iPhone, according to Forbes. When the application is launched, the user enters sensitive data to access their accounts and thereby gives hackers access to it.
One of the most famous examples of hacking attacks of this type were traders of the American cryptocurrency exchange Poloniex, which downloaded mobile applications posted by hackers on Google Play, pretending to be a mobile gateway for the popular crypto exchange. However, the Poloniex team had not developed applications for Android and didn’t have links to any mobile apps.
Users of iOS devices aren’t immune but are more protected. Apple was forced to tighten the rules for admission of applications to its store in order to somehow suspend the distribution of such software. This is a completely different story; the damage from the hacking of wallets is much more severe, this way the miner only slows down the computer operations.
Top Tips
- Only install apps you need and have credible ratings and reviews
- Add two-factor authorization-identification on all apps, on all devices, all the time
- Check all links are genuine
Sites-clones and phishing
The oldest form and around since the “dot-com revolution,” or the dawn of true digital tech. As they say “the old ones are the best.” In the first case, attackers replicate to the near letter, an original website’s domain that is not quite the same. The goal of such a trick — including the substitution of the address in the browser address field — is to lure a user to the site-clone and force them to enter the account’s password or a secret key.
In the second case, they send an email that — by design — identically copies the letters of the official project, but — in fact — aims to force you to click the link and enter your personal data. It’s been reported that this method has led to $225 million in cryptocurrency being stolen.
Top Tips
- If something feels wrong or suspicious, close and delete accordingly
- Only interact with a crypto related site with genuine HTPPS protocol
Public Wi-Fi
This is probably the most naturally feared type of hacking by the average person. Put in very simple terms, the user’s device reconnects to the same Wi-Fi network of hackers due to a link or false Wi-Fi network choice. All the information downloaded or sent through the network by a user is available to attackers, especially the private keys from crypto wallets amongst other private details such as online banking and email passwords etc. This problem is especially urgent for public Wi-Fi networks at railway stations, airports, hotels and places where large groups of people visit and where a hacker can sit and wait incognito for one unsuspecting victim.
Top tips
- Never use public Wi-Fi for cryptocurrency transactions, even with VPM
- Update your own router firmware due to consistent manufacture releases
Bots in Slack
Slack has recently been valued at about $5bn so it’s not going anywhere fast. Slack is a corporate messenger application service but since mid-2017, Slack bots have been used for stealing crypto. Typically, hackers create a bot that notifies users about problems with their cryptos causing panic and fear (understandably). The goal is to force a person to click the link and enter a private key and, in the process, takes all details. They are then blocked by users.
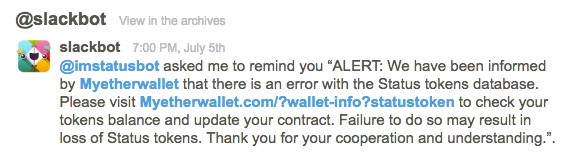
The largest successful attack by hackers through Slack is considered to be the Enigma group hack – a rogue Slack bot, defrauded a total of $500,000 in Ethereum from unsuspecting users.
Top Tips
- Report suspicious activity and block where appropriate
- Ignore needless, irrelevant activity
- Use anti-virus software or built-in Google safe browsing
Add-ons for crypto trading
Any Internet browser offer extensions to customize the user interface to what and how they wish for more comfortable work. You can also customise and add exchanges and wallets. The issue is not even that add-ons read everything that you are typing while using the internet, but that extensions are developed in JavaScript, which makes them extremely vulnerable to hacking attacks. JavaScript’s vulnerabilities have become highly prevalent in organizations, especially Indian ones. In addition, many extensions could be used for hidden mining, due to the user’s computing resources. All of which is unknown to the user at the time.
Top tips
- Use a separate browser for crypto activity
- Go incognito on the browser
- Don’t download any add-ons. Ever
- If you can afford it, get a separate device or machine for crypto trading
- Download antivirus and network protection
Authentication by SMS
SMS is probably the most preferred method of authentication because they are used to doing it, its fast, on the mobile and randomised each time its performed. Positive Technologies, a company that specializes in cybersecurity, has demonstrated how easy it is to intercept an SMS with a password confirmation, transmitted practically worldwide by the Signaling System 7 (SS7) protocol. During a demonstration using the example of Coinbase accounts, experts intercepted the message and stolen the relevant data thanks to their own software they’ve developed. At a glance, this looks like a Coinbase vulnerability, which is partly true but the real weakness is in the cellular system itself. This proved that any system can be accessed directly via SMS, even if 2FA is used its just a matter of having the correct software.
Top tips
- Turn off call forwarding to deny data access
- Down use two-factor authorisation on the phone, use a software solution
Featured image: © metamorworks – stock.adobe.com